微積分上課筆記2
本文最後更新於:2022年11月18日 凌晨
微積分上課筆記
- 2022/11/16
One to one function
for every $y$, there is only at most one $x$ satisfies $f(x) = y$.
例題
$f(x)=\sqrt{-1-x}$ $\rightarrow x \leq -1$ => $f^{-1}(x)=-1-x^2$
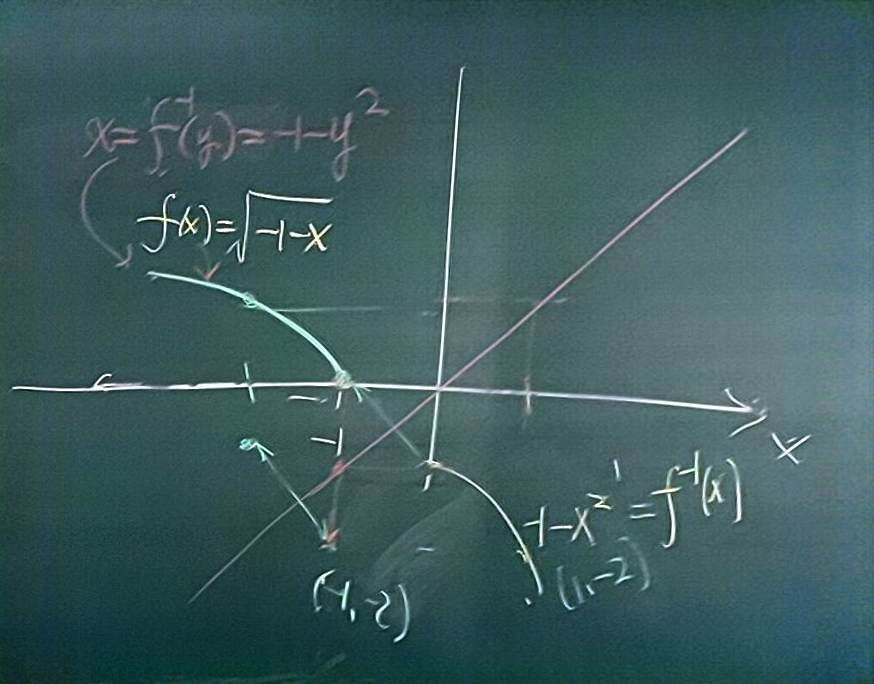
The Calculus of Inverse Functions
Theorem. If $f$ is a one-to-one continuous function defined on an interval, then its inverse function is also continuous.
$\frac{df^{-1}(f(x))}{dx}=\frac{dx}{dx}=1$
$\rightarrow \frac{d}{dx} f^{-1}(f(x)) \times \frac{df}{dx}=1$
$\rightarrow f’(f^{-1}(x))\times \frac{df^{-1}(x)}{dx}=1$
$\rightarrow \frac{df^{-1}(x)}{dx} = \frac{1}{f’(f^{-1}(x))}$
重要
例題
If $f(x)=2x+cosx$ ,
find $(f^{−1})′(1)$
$y=f(x)=2x + cos(x)$
not easy to find the explicit form of $f^{-1}(x)$
$f’=2-sinx$
=> $f$ is increase function => one-to-one
=>$f^{-1}$exists
The Natural logarithmic Function
$ln(x)=\int_1^x \frac{1}{x},x > 0$
Laws
- $ln(xy)=ln(x) + ln(y)$
- $ln(\frac{x}{y}) = ln(x) - ln(y)$
- $ln(x^r) = rln(x)$
$ln(x)=\int_1^x \frac{1}{t}dt$
$\frac{d}{dx}ln(x) = \frac{d}{dx} \int_1^x \frac{1}{t}dt=\frac{1}{x}$,due to $ln(1)=0$
Proof rule 1
因為$ln(x)$和$ln(ax)$有相同導數
$ln(x) + C = ln(ax)$
=> $let$ $x = 1$
=>$0 + C = ln(a)$
=>$C = ln(a)$
Proof rule 3
因為$ln(x)$和$ln(x^r)$有相同導數
$ln(x) + C = ln(x^r)$
$let$ $x = 1$
=> $0 + C = 0$
=>$C = 0$
=>$ln(x) = ln(x^r)$
$e$
$e$ is the number such that $ln(e)= 1$
$e \rightarrow 1.71828$